1. Spring的工厂类
ApplicationContext是继承自BeanFactory的。BeanFactory是一个老版本的工厂类,只有在调用getBean方法时,才会生成类的实例。
ApplicationContext工厂在加载配置文件时,就会将Spring管理的类都实例化。
加载配置文件一般使用以下两个实现类:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:加载类路径下的配置文件(src下)FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:加载文件系统下的配置文件(磁盘下的文件)
2. Spring的Bean管理(XML方式)
2.1 使用类构造器实例化(默认无参数)
- 编写Bean1类:
/**
* Bean的实例化的三种方式:采用无参数的构造方法的方式
*/
public class Bean1 {
public Bean1(){
System.out.println("Bean1被实例化了...");
}
}
- 在xml中配置如下内容:
<!-- Bean的实例化的三种方式-->
<!-- 第一种:无参构造器的方式-->
<bean id="bean1" class="com.zero.ioc.demo1.Bean1"></bean>
- 在测试方法中加载对象,并完成实例化
@Test
public void test1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
}
2.2 使用静态工厂方法实例化(简单工厂模式)
- 编写Bean2类
/**
* Bean的实例化的三种方式:使用静态工厂方法实例化
*/
public class Bean2 {
}
- 编写静态工厂类
// Bean2的静态工厂
public class Bean2Factory {
public static Bean2 createBean2(){
System.out.println("Bean2Factory已执行...");
return new Bean2();
}
}
- 配置xml
<!-- 第二种:静态工厂的方式-->
<bean id="bean2" class="com.zero.ioc.demo1.Bean2Factory" factory-method="createBean2"/>
- 测试
@Test
public void test2(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Bean2 bean2 = (Bean2) context.getBean("bean2");
}
JDK12和Spring3.2不兼容!!!在使用静态工厂方法实例化对象时,会导致
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException异常,更换Spring版本至4.2即可。
2.3 使用实例工厂方法实例化(工厂方法模式)
- 编写Bean3类
/**
* Bean的实例化三种方式:实例工厂实例化
*/
public class Bean3 {
}
- 编写实例工厂类
public class Bean3Factory {
public Bean3 createBean3(){
System.out.println("Bean3Factory执行了...");
return new Bean3();
}
}
- 配置xml
<!-- 第三种:实例工厂的方式-->
<bean id="bean3Factory" class="com.zero.ioc.demo1.Bean3Factory"/>
<bean id="bean3" factory-bean="bean3Factory" factory-method="createBean3"/>
- 测试
@Test
public void test3(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Bean3 bean3 = (Bean3) context.getBean("bean3");
}
2.4 Bean的配置
- id和name
- 一般情况下,装配一个Bean时,通过指定一个id属性作为Bean的名称
- id属性在IOC容器中必须是唯一的
- 如果Bean的名称中含有特殊字符,就需要使用name属性
- class
- class用于设置一个类的完全路径名称,主要作用是IOC容器生成类的实例
2.5 Bean的作用域
| 类别 | 说明 |
|---|---|
singleton |
在SpringIOC容器中仅存在一个Bean实例,Bean以单实例的方式存在 |
prototype |
每次调用getBean()时都会返回一个新的实例 |
request |
每次HTTP请求都会创建一新的Bean,该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
session |
同一个HTTP Session共享一个Bean,不同的HTTP Session使用不同的Bean。该作用域仅适用于WebApplicationContext环境 |
- 在xml中配置
<!-- Bean的作用范围-->
<!--仅存在一个Bean实例,单实例-->
<bean id="person" class="com.zero.ioc.demo2.Person" scope="singleton"/>
<!--每次调用getBean()都会返回一个新实例-->
<bean id="person" class="com.zero.ioc.demo2.Person" scope="prototype"/>
2.6 Spring容器中Bean的生命周期
Spring初始化bean或销毁bean时,有时需要作一些处理工作,因此spring可以在创建和拆卸bean时调用bean的两个生命周期方法。
<bean id="xxx" class="xxx"
init-method="init"
destroy-method="destroy"/>
<!--
当bean被载入到容器时调用init
当bean从容器中删除时调用destroy(必须是单例bean才会自动调用,即scope="singleton"才有效)
-->
web容器中会自动调用,但是main函数或测试用例需手动调用。
- 示例,创建一个man类
public class Man {
public Man(){
System.out.println("Man被实例化了");
}
public void setup(){
System.out.println("Man被初始化了");
}
public void myDestroy(){
System.out.println("Man被销毁了");
}
}
- 配置xml
<bean id="man" class="com.zero.ioc.demo2.Man" init-method="setup" destroy-method="myDestroy"/>
- 测试
@Test
public void test2(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Man man = (Man) context.getBean("man");
context.close();
}
2.6.1 Bean完整生命周期过程
完整生命周期总共有11个步骤。
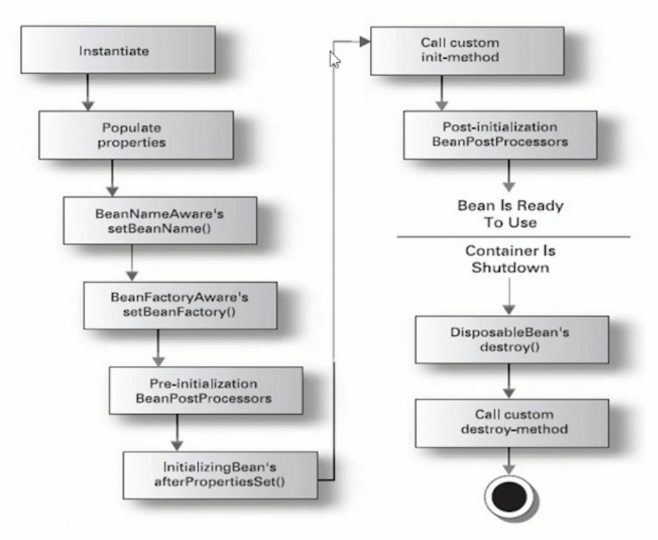
instantiate bean,对象实例化populate properties,封装属性- 如果Bean实现
BeanNameAware执行setBeanName - 如果Bean实现
BeanFactoryAware或者ApplicationContextAware设置工厂setBeanFactory或者上下文对象setApplicationContext - 如果存在类实现
BeanPostProcessor(后处理Bean),执行postProcessBeforeInitialization - 如果Bean实现
InitializingBean执行afterPropertiesSet - 调用
<bean init-method="init">指定初始化方法init - 如果存在类实现
BeanPostProcessor(处理Bean),执行postProcessAfterInitialization - 执行业务处理
- 如果Bean实现
DisposableBean执行destroy - 调用
<bean destroy-method="customerDestroy">指定销毁方法customerDestroy
代码演示:
- 编写man类
public class Man implements BeanNameAware, ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("第二步:设置属性");
this.name = name;
}
public Man(){
System.out.println("第一步:实例化。。。");
}
public void setup(){
System.out.println("第七步:Man被初始化了");
}
public void myDestroy(){
System.out.println("第十一步:执行自己定义的销毁方法");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("第三步:设置Bean的名称"+s); // 就是xml中配置的id的值
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第四步:了解工厂信息");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("第六步:属性设置后执行 ");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("第九步:执行业务方法 ");
}
public void destroy() throws Exception{
System.out.println("第十步:执行Spring的销毁方法");
}
}
- 编写
MyBeanPostProcessor类
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第五步:初始化前方法。。。");
return o;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("第八步:初始化后方法。。。");
return o;
}
}
- 配置xml
<bean id="man" class="com.zero.ioc.demo2.Man" init-method="setup" destroy-method="myDestroy">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.zero.ioc.demo2.MyBeanPostProcessor"/>
- 测试
@Test
public void test2(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Man man = (Man) context.getBean("man");
man.run();
context.close();
}
/**
输出结果:
第一步:实例化。。。
第二步:设置属性
第三步:设置Bean的名称man
第四步:了解工厂信息
第五步:初始化前方法。。。
第六步:属性设置后执行
第七步:Man被初始化了
第八步:初始化后方法。。。
第九步:执行业务方法
8月 06, 2019 7:48:41 下午 org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext doClose
信息: Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@7823a2f9: startup date [Tue Aug 06 19:48:41 CST 2019]; root of context hierarchy
第十步:执行Spring的销毁方法
第十一步:执行自己定义的销毁方法
*/
3. Spring的属性注入(XML方式)
对于类成员变量,注入方式有三种:构造函数注入、属性setter方法注入、接口注入
Spring支持前两种
3.1 属性注入-构造方法注入
通过构造方法注入Bean的属性值或依赖的对象,它保证了Bean实例在实例化后就可以使用。
构造器注入通过
<constructor-arg>元素来声明属性代码示例
- 创建user类
public class User { private String name; private Integer age; public User(String name, Integer age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }- 配置xml
<!-- Spring属性注入-通过构造方法注入--> <bean id="user" class="com.zero.ioc.demo3.User"> <constructor-arg name="name" value="张三"/> <constructor-arg name="age" value="22"/> </bean>- 测试
public class demo3Test { @Test public void test1(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); User user = (User) context.getBean("user"); System.out.println(user); } }
3.2 属性注入-set方法注入
使用set方法注入,在Spring配置文件中,通过
<property>设置注入的属性代码示例
- 创建person类
public class Person { private String name; private Integer age; private Cat cat; // 省略get/set方法 @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", cat=" + cat + '}'; } }- 创建cat类
public class Cat { private String name; @Override public String toString() { return "Cat{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } // 省略get/set方法 }- 配置xml
<!-- Spring属性注入-通过set方法注入--> <bean id="person" class="com.zero.ioc.demo3.Person"> <property name="name" value="李四"/> <property name="age" value="25"/> <!-- ref可以引入其他bean的id或name--> <property name="cat" ref="cat"/> </bean> <bean id="cat" class="com.zero.ioc.demo3.Cat"> <property name="name" value="ketty"/> </bean>- 测试
@Test public void test2(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Person person = (Person) context.getBean("person"); System.out.println(person); // Person{name='李四', age=25, cat=Cat{name='ketty'}} }
普通类型的值使用value设置值,对象类型的值使用ref。
3.3 属性注入-p名称空间
使用p命名空间:为了简化xml文件配置,Spring从2.5开始引入一个新的p名称空间。
语法:p:<属性名>="xxx" 引入常量值,p:<属性名>-ref="xxx"引用其他Bean对象
- 示例,配置xml,
<!--先在beans中添加:xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p",引入p命名空间-->
<!-- Spring属性注入-通过p名称空间注入-->
<!--修改原有的person配置如下,即可实现通过p名称空间注入-->
<bean id="person" class="com.zero.ioc.demo3.Person" p:name="赵钱" p:age="26" p:cat-ref="cat"/>
<bean id="cat" class="com.zero.ioc.demo3.Cat" p:name="小黑"/>
3.4 属性注入-SpEL注入
SpEL:spring expression language,Spring表达式语言,对依赖注入进行简化- 语法:
#{表达式},<bean id="" value="#{表达式}"/>
Spel表达式语法:
基本语法:#{}
#{'hello'}:使用字符串
#{beanId}:使用另一个bean
#{beanId.method()}:指定bean和对应方法,并执行方法
#{T(java.lang.Math).PI}:使用静态字段或方法
- 示例如下,创建Product和Category类用于测试
public class Product {
private String name;
private Double price;
private Category category;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Product{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", category=" + category +
'}';
}
// 省略get/set方法
}
public class Category {
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Category{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
// 省略get/set方法
}
- 创建简单的计算类
public class ProductInfo {
public Double addPrice(){
return Math.random() * 20;
}
}
- 配置xml
<!-- Spring属性注入-通过SpEL注入-->
<bean id="category" class="com.zero.ioc.demo3.Category">
<property name="name" value="#{'水果'}"/>
</bean>
<bean id="productInfo" class="com.zero.ioc.demo3.ProductInfo"/>
<bean id="product" class="com.zero.ioc.demo3.Product">
<property name="name" value="#{'西瓜'}"/>
<property name="price" value="#{productInfo.addPrice()}"/>
<property name="category" value="#{category}"/>
</bean>
- 测试
@Test
public void test3(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
Product product = (Product) context.getBean("product");
System.out.println(product);
}
3.5 复杂类型的属性注入
- 数组类型的属性注入
- List集合类型的属性注入
- Set集合类型的属性注入
- Map集合类型的属性注入
Properties类型的属性注入
代码示例如下:
- 创建集合类CollectionBean
`java
public class CollectionBean {private String[] arrs; // 数组类型 private List<String> list; // List集合类型 private Set<String> set; // Set集合类型 private Map<String,Integer> map; // Map集合类型 private Properties properties; // 属性类型
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean{" +
"arrs=" + Arrays.toString(arrs) +
", list=" + list +
", set=" + set +
", map=" + map +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
// 省略get/set方法
}
- 配置xml,添加如下内容
```xml
<!-- 复杂类型的属性注入-->
<bean id="collectionBean" class="com.zero.ioc.demo4.CollectionBean">
<!-- 数组类型的属性注入-->
<property name="arrs">
<list>
<value>aaa</value>
<value>bbb</value>
<value>ccc</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- List集合类型的属性注入-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>111</value>
<value>222</value>
<value>333</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- set集合类型的属性注入-->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>ddd</value>
<value>eee</value>
<value>fff</value>
</set>
</property>
<!-- map集合类型的属性注入-->
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="aaa" value="111"/>
<entry key="bbb" value="222"/>
<entry key="ccc" value="333"/>
</map>
</property>
<!-- Properties类型的属性注入-->
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="username">root</prop>
<prop key="password">123456</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
测试
@Test public void test1(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); CollectionBean collectionBean = (CollectionBean) context.getBean("collectionBean"); System.out.println(collectionBean); }
4. Spring的Bean管理(注解方式)
4.1 使用注解定义Bean
- Spring2.5 引入使用注解去定义Bean
@Component,描述Spring框架中的Bean
- 除了
@Component外,Spring还提供了3个功能基本等效的注解@Repository:用于对DAO实现类进行标注@Service:用于对Service实现类进行标注@Controller:用于对Controller实现类进行标注
这三个注解是为了让标注类本身的用途更加清晰,Spring在后续版本会对其增强。
代码示例
- 创建
UserService类
/** * Spring的Bean管理的注解方式: * 传统方式:需要去XML中配置<bean id="" class=""></bean> * */ @Service("userService") public class UserService { public String hello(String name){ return "Hello" + name; } }- 配置xml,开启扫描
`xml
<?xml version=”1.0” encoding=”UTF-8”?><!-- 开启注解扫描 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.zero.demo1"/>- 创建
- 测试
```java
@Test
public void demo1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
String hello = userService.hello("小明");
System.out.println(hello);
}
5. Spring的属性注入(注解方式)
- 使用
@Autowired进行自动注入 @Autowired默认按照类型进行注入- 如果存在两个相同Bean类型相同,则按照名称注入
@Autowired注入时可以针对成员变量或者set方法- 通过
@Autowired的required属性,设置一定要找到匹配的Bean - 使用
@Qualifier指定注入Bean的名称 使用
Qualifier指定Bean名称后,注解Bean必须指定相同名称代码示例:
- 创建一个dao
@Repository("userDao") public class UserDao { public void save(){ System.out.println("Dao中保存用户。。。"); } }- 修改UserService
@Service("userService") public class UserService { //使用value直接对属性值进行注入 @Value("苹果") private String something; // 自动注入 @Autowired @Qualifier("userDao") // 指定注解的Bean名称必须相同‘ @Resource(name="userDao") // 可以使用@Resource,指定Bean名称 private UserDao dao; public String hello(String name){ return "Hello" + name; } public void eat(){ System.out.println("eat:"+something); } public void save(){ System.out.println("Service中保存用户。。。"); dao.save(); } }- 测试
@Test public void demo2(){ ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); userService.save(); }
- Spring提供对JSR-250中定义
@Resource标准注解的支持@Resource和@Autowired注解功能相似- 如无法使用
@Resource,需在pom.xml中引入javax.annotation-api依赖
5.1 Spring的其他注解
Spring初始化Bean或销毁bean时,有时需要作一些处理工作,因此spring可以在创建和拆卸bean时调用bean的两个生命周期方法。
<bean id="xxx" class="xxx"
init-method="setup"
destroy-method="teardown"/>
<!--
当bean被载入到容器时调用setup,注解方式:@PostConstruct,初始化
当bean从容器中删除时调用teardown(必须是单例bean才会自动调用,即scope="singleton"才有效)
注解方式:@PreDestroy,销毁
-->
- 代码示例,创建bean1类
@Component("bean1")
public class Bean1 {
// 生命周期注解,初始化
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("initBean...");
}
public void say(){
System.out.println("say...");
}
// 生命周期注解,销毁
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("destroyBean...");
}
}
- 配置xml
<!-- 开启注解扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zero"/>
- 测试
@Test
public void test1(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Bean1 bean1 = (Bean1) context.getBean("bean1");
bean1.say();
context.close();
}
5.2 Bean的作用范围
- 使用注解配置的Bean和
<bean>配置的一样,默认作用范围都是singleton @Scope注解用于指定Bean的作用范围代码示例:
- 创建bean2类,设置其作用范围
@Component("bean2") @Scope("prototype") // 设置作用范围,使用多例创建对象 public class Bean2 { }- 测试
@Test public void test2(){ ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); Bean2 bean1 = (Bean2) context.getBean("bean2"); Bean2 bean2 = (Bean2) context.getBean("bean2"); System.out.println(bean1 == bean2); }
5.3 传统XML配置和注解配置混合使用
- XML方式的优势
- 结构清晰,易于阅读
- 注解方式的优势
- 开发便捷,属性注入方便
XML与注解的整合开发
- 引入context命名空间
- 在配置文件中添加
<context:annotation-config/>
代码示例
- 创建
ProductService,ProductDao,CategoryDao,均创建简单的save方法。
`java
public class ProductService {// 使用注解 @Resource(name = "categoryDao") private CategoryDao categoryDao; @Resource(name = "productDao") private ProductDao productDao;// public void setCategoryDao(CategoryDao categoryDao) {
// this.categoryDao = categoryDao;
// }
//
// public void setProductDao(ProductDao productDao) {
// this.productDao = productDao;
// }public void save(){ System.out.println("ProductService中的save方法执行了..."); categoryDao.save(); productDao.save(); }}
public class ProductDao {
public void save(){ System.out.println("ProductDao中的save方法执行了..."); }}
- 创建
public class CategoryDao {
public void save(){
System.out.println(“CategoryDao中的save方法执行了…”);
}
}
- 配置xml
```xml
<!--单独开启注解功能-->
<context:annotation-config/>
<bean id="productService" class="com.zero.demo3.ProductService">
<!-- <property name="productDao" ref="productDao"/>-->
<!-- <property name="categoryDao" ref="categoryDao"/>-->
</bean>
<bean id="productDao" class="com.zero.demo3.ProductDao"/>
<bean id="categoryDao" class="com.zero.demo3.CategoryDao"/>
- 测试
@Test
public void test1() {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
ProductService productService = (ProductService) context.getBean("productService");
productService.save();
}

