1. JDBC
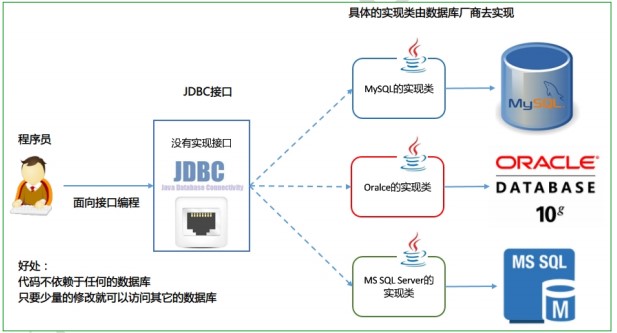
Java数据库连接(Java DataBase Connectivity),简称JDBC。是一种用于执行SQL语句的Java API,可以为多种关系数据库提供统一访问,它由一组Java语言编写的类好接口组成。
1.1 客户端操作MySQL数据库的方式
- 使用第三方客户端访问:SQLyog、Navicat、SQLWave、MyDB Studio等等
- 使用MySQL自带的命令行方式
- 通过Java API来访问MySQL数据库
1.2 什么是JDBC
JDBC本质:其实是官方(sun公司)定义的一套操作所有关系型数据库的规则,即接口。各个数据库厂商去实现这套接口,提供数据库驱动jar包。我们可以使用这套接口(JDBC)编程,真正执行的代码是驱动jar包中的实现类。
- 使用JDBC的好处
- 如果要开发访问数据库的程序,只需会调用JDBC接口中的方法即可,不用关注类具体实现
- 使用同一套Java代码,进行少量的修改就可以访问其他JDBC支持的数据库了
1.3 使用JDBC开发使用到的包
| 使用的包 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| java.sql | 所有与JDBC访问数据库相关的接口和类 |
| javax.sql | 数据库扩展包,提供数据库额外的功能。如连接池 |
| 数据库的驱动 | 由各大数据库厂商提供,需要额外去下载,是对JDBC接口实现的类 |
1.4 JDBC的核心API
| 接口或类 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| DriverManager类 | 1. 管理和注册数据库驱动;2. 得到数据库连接对象 |
| Connection接口 | 一个连接对象,可用于创建Statement和PreparedStatement对象 |
| Statement接口 | 一个SQL语句对象,用于将SQL语句发送给数据库服务器 |
| PrepareStatement接口 | 一个SQL语句对象,是Statement的子接口 |
| ResultSet接口 | 用于封装数据库查询的结果集,返回给客户端Java程序 |
1.5 导入驱动Jar包
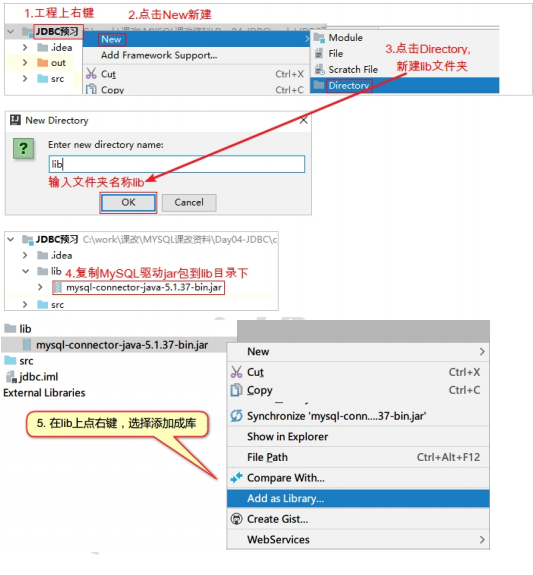
1.6 加载和注册驱动
| 加载和注册驱动的方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Class.forName(数据库驱动实现类) | 加载和注册数据库驱动,数据库驱动由mysql厂商提供:”com.mysql.jdbc.Driver” |
从JDBC3开始,弃用了驱动类“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”,新的驱动程序类是“com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver”。驱动程序是通过SPI自动注册的,通常不需要手动加载驱动程序类。
2. DriverManager类
驱动管理对象类,该类的作用是管理和注册驱动,以及创建数据库的连接。
注:mysql5之后的驱动jar包可以省略注册驱动的步骤。
2.1 获取数据库连接
Connection getConnection(String url,String user,String password):通过连接字符串,用户名,密码来得到数据库的连接对象Connection getConnection(String url,Properties info):通过连接字符串,属性对象来得到连接对象参数说明:
| 参数列表 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 用户名 | 登录的用户名 |
| 密码 | 登录的密码 |
| 连接字符串URL | 不同的数据库URL是不同的,MySQL的写法:jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/数据库名[?参数名=参数值] |
| 驱动类的字符串名 | com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver |
- 连接数据库URL地址格式:
协议名:子协议://服务器名或IP地址:端口号/数据库名?参数=参数值&参数2=值2
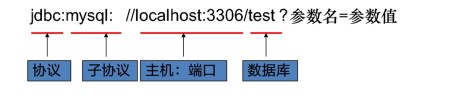
在本地服务器的情况下:MySQL中可简写为
jdbc:mysql:///数据库名
- 乱码问题处理
如果数据库出现乱码,可以指定参数:?characterEncoding=utf8,表示让数据库以UTF-8编码来处理数据。
2.2 快速入门
- 使用用户名、密码、URL来得到连接对象
public class Demo01JDBC { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ // 1. 导入jar驱动包 // 2.注册驱动 Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // com.mysql.jdbc.Driver已弃用,且该语句jdbc3后可省略 // 3. 使用用户名密码来获取数据库连接对象 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1?serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "123456"); // 4. 定义sql语句 String sql = "update account set balance=1000 where id=1"; // 5. 获取执行sql语句的对象 Statement stat = conn.createStatement(); // 6. 执行sql语句 int count = stat.executeUpdate(sql); // 7. 处理结果 System.out.println(count); // 8. 释放资源 stat.close(); conn.close(); } }
从JDBC3开始,弃用了驱动类“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”,新的驱动程序类是“com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver”。驱动程序是通过SPI自动注册的,通常不需要手动加载驱动程序类。
- 使用属性文件和URL得到连接对象
`java
public class Demo02JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
}// 1. 定义URL连接字符串 String url = "jdbc:mysql:///db1?serverTimezone=UTC"; // 本地服务器且端口号3306.故省略 // 2. 创建属性对象 Properties info = new Properties(); // 3. 将用户名和密码放入info对象中 info.setProperty("user","root"); info.setProperty("password","123456"); // 4. 通过属性文件来获取数据库连接对象 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, info); System.out.println(conn); // com.mysql.cj.jdbc.ConnectionImpl@51cdd8a:获取的是连接对象的内存地址值
}
## 3. Connection接口
Connection 接口,具体的实现类由数据库的厂商实现,代表一个连接对象。
### 3.1 主要方法
- 获取执行sql的对象:
- `Statement createStatement(String sql)`
- `PreparedStatement preparedStatement(String sql)`
- 管理事务:
- 开启事务:`setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit)`:调用该方法设置参数为fasle,即开启事务
- 提交事务:`commit()`
- 回滚事务:`rollback()`
## 4. Statement接口
用于执行静态SQL语句并返回其生成的结果对象
### 4.1 主要方法
1. `boolean execute(String sql)`:可以执行任意的sql
2. `int executeUpdate(String sql)`:执行DML(insert、update、delete)语句、DDL(create、alter、drop)语句。返回值:**影响的行数**,可以通过判断行数来确定语句是否执行成功。
3. `ResultSet executeQuery(String sql)`:执行DQL(select)语句。返回结果集对象
### 4.2 演示案例
1. account表中添加一条记录,使用insert语句
```java
public class Demo03JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Statement stmt = null;
Connection conn = null;
try {
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 定义sql
String sql = "insert into account values(null,'小王',3000)";
// 3. 获取连接数据库对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db1?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=gbk", "root", "123456");
// 4. 获取执行sql的对象 Statement,并传入sql语句执行
stmt = conn.createStatement();
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // 返回值影响的行数
// 5. 处理结果
if (count>0)
System.out.println("添加成功");
else
System.out.println("添加失败");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//stmt.close();
// 避免空指针异常
if(stmt!=null && conn!=null){
try {
stmt.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
修改一条表记录
// 只需在上述代码基础上改动sql语句即可 String sql = "update account set balance=2000 where name='小王'"; conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db1?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=gbk", "root", "123456"); stmt = conn.createStatement(); int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql); // 返回值影响的行数 if (count>0) System.out.println("修改成功"); else System.out.println("修改失败");删除一条表记录
// 改动sql语句即可 public class DelJDBC { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db1?serverTimezone=UTC","root","123456"); stmt = conn.createStatement(); int count = stmt.executeUpdate("delete from account where id=3"); if (count>0) System.out.println("delete success!"); else System.out.println("delete failed!"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { if (stmt!=null && conn!=null) { try { stmt.close(); conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
5. ResultSet接口
结果集对象,封装查询的结果
5.1 主要方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
boolean next() |
游标向下移动1行,返回布尔类型,如果还有下一条记录返回true,反之false |
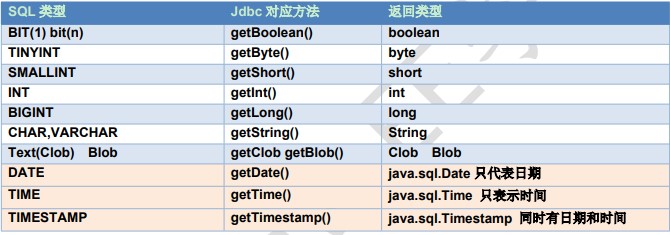
数据类型 getXxx() |
通过字段名或是列编号,填入参数String或是整数(1开始),返回不同的类型。 |
常用数据类型转换表
5.2 方法演示
public class DQLJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ResultSet rs = null;
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db1?serverTimezone=UTC","root","123456");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from account");
// 处理结果
while (rs.next()){ // 循环判断游标是否是最后一行末尾
int id = rs.getInt(1); // 通过列编号获取数据
String name = rs.getString("name"); // 通过列名获取
double balance = rs.getDouble(3); // 通过列编号获取
System.out.println(id+","+name+","+balance);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt!=null){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}if (conn!=null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
5.3 练习
- 定义一个方法:查询users表的数据将其封装为对象,然后装载集合,返回。
// 定义存储数据的类
public class Users {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private String site;
// 省略构造方法等
}
// 定义方法类,实现方法
public class Demo5JDBC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Users> list = new Demo5JDBC().findAll();
System.out.println(list);
}
// 创建方法,查询所有users对象,返回一个list
public List<Users> findAll(){
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
List<Users> list = null;
try {
// 1. 注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
// 2. 获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db5?serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "123456");
// 3. 获取执行sql对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 4. 执行sql
rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from users");
// 5. 遍历结果集,封装对象,装载集合
Users us = null;
list = new ArrayList<>();
while (rs.next()){
// 获取数据
int id = rs.getInt("id");
String name = rs.getString("name");
int age = rs.getInt("age");
String site = rs.getString(4);
// 创建users对象,并赋值
us = new Users();
us.setId(id);
us.setName(name);
us.setAge(age);
us.setSite(site);
// 装载集合
list.add(us);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 释放资源,rs,stmt和conn
if (rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 省略其他两个,与上方法一样
}
return list;
}
}
6. 自定义数据库工具类JdbcUtils
可以把经常用到的功能做成一个工具类,在不同的地方重用。
6.1 主要方法
- 可以把几个字符串定义成常量:用户名,密码,URL,驱动类
- 得到数据库的连接:
getConnection() - 关闭所有打开的资源:
close(Connection conn,Statement stmt,ResultSet rs)和close(ResultSet rs,Statement stmt, Connection conn)
6.2 使用工具类将上一个练习优化
定义工具类
在项目目录下新建一个util文件夹,然后新建JDBCUtils.java文件,编写如下内容。`java
// JDBC工具类
public class JDBCUtils {
private static String url;
private static String user;
private static String password;
private static String driver;// 文件的读取,只需读取一次即可拿到这些值:使用静态代码块
static {// 读取资源文件,获取配置值 try { // 1. 创建Properties集合类 Properties pro = new Properties(); // 获取src路径下的文件的方式-->ClassLoader 类加载器,如此就可以动态的获取src的绝对路径 ClassLoader classLoader = JDBCUtils.class.getClassLoader(); URL resource = classLoader.getResource("jdbc.properties"); String path = resource.getPath(); System.out.println(path); // 2. 加载文件// pro.load(new FileReader(“src/jdbc.properties”));
pro.load(new FileReader(path)); // 3. 获取属性,赋值 url = pro.getProperty("url"); user = pro.getProperty("user"); password = pro.getProperty("password"); driver = pro.getProperty("driver"); // 4. 注册驱动 Class.forName(driver); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }}
// 获取连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);}
// 释放资源
public static void close(Statement stmt, Connection conn){if (stmt!=null){ try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}
// 释放资源重载
public static void close(ResultSet rs,Statement stmt, Connection conn){if (rs!=null){ try { rs.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (stmt!=null){ try { stmt.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if (conn!=null){ try { conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}
}
2. 定义配置文件
在项目源文件src下新建`jdbc.properties`文件。
```properties
url=jdbc:mysql:///db5?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=gbk
user=root
password=123456
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
演示用法
public class Demo6JDBCUtil { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Users> list = new Demo6JDBCUtil().findAll2(); System.out.println(list); } /** * 演示JDBC工具类 * @return */ public List<Users> findAll2(){ Connection conn = null; Statement stmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; List<Users> list = null; try { // // 1. 注册驱动 // Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // // 2. 获取连接 // conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///db5?serverTimezone=UTC", "root", "123456"); conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection(); // 3. 获取执行sql对象 stmt = conn.createStatement(); // 4. 执行sql rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from users"); // 5. 遍历结果集,封装对象,装载集合 Users us = null; list = new ArrayList<>(); while (rs.next()){ // 获取数据 int id = rs.getInt("id"); String name = rs.getString("name"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String site = rs.getString(4); // 创建users对象,并赋值 us = new Users(); us.setId(id); us.setName(name); us.setAge(age); us.setSite(site); // 装载集合 list.add(us); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JDBCUtils.close(rs,stmt,conn); // 直接调用方法就可以释放资源 } return list; } }
6.3 练习:登录案例
- 创建用户表
- 获取用户输入
- 查询数据库,与数据库中数据进行匹配
- 返回结果
public class LoginExercise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取用户输入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入用户名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.nextLine();
if (name==null || pwd==null)
System.out.println("输入内容不能为空");
login(name,pwd);
sc.close();
}
public static void login(String name,String pwd){
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 连接数据库,判断是否存在数据
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
stmt = conn.createStatement();
rs = stmt.executeQuery("select * from users where name='"+name+"' and pwd='"+pwd+"'");
if (rs.next()) // 返回布尔值,true则存在,false则不存在
System.out.println("登录成功");
else
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs,stmt,conn);
}
}
}
7. PreparedStatement接口
表示预编译的 SQL 语句的对象。 SQL 语句被预编译并存储在 PreparedStatement 对象中。然后可以使用此对象多次高效地执行该语句。
7.1 SQL注入问题
在拼接sql时,如果有一些sql的特殊关键字参与字符串的拼接,会造成安全性问题。
- 输入密码时,如果输入以下密码,在账户和密码不正确情况下也登录成功

- 原因
打印了一下查询的SQL语句:select * from user where name='ehwqhwqek' and pwd='a' or '1'='1';发现当and前面为假,但是or后面为真,语句实际相当于:select * from user where true;查询了所有记录
要解决 SQL 注入就不能让用户输入的密码和我们的 SQL 语句进行简单的字符串拼接。
7.2 解决SQL注入问题
使用PreparedStatement对象来解决该问题
- 预编译的SQL:参数使用?作为占位符,例:
select * from users where name = ? and pwd = ? - 给?赋值方法:
setXxx(?的位置编号(1开始),?的值)
7.2.1 方法演示
// 使用prepardStatement对象解决sql注入问题
public class LoginExercise2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取用户输入
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入用户名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入密码:");
String pwd = sc.nextLine();
if (name==null || pwd==null)
System.out.println("输入内容不能为空");
login(name,pwd);
sc.close();
}
/*
登录方法,使用PreparedStatement实现
*/
public static void login(String name,String pwd){
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 连接数据库,判断是否存在数据
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
// 定义sql语句
String sql = "select * from users where name = ? and pwd = ?";
// 获取执行sql对象
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql); // 将sql传入,进行预编译
// 给?赋值
ps.setString(1,name);
ps.setString(2,pwd);
rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) // 返回布尔值,true则存在,false则不存在
System.out.println("登录成功");
else
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtils.close(rs,ps,conn);
}
}
}
7.3 PreparedStatement原理

7.3.1 优点
prepareStatement()会先将 SQL 语句发送给数据库预编译。PreparedStatement会引用着预编译后的结果。可以多次传入不同的参数给PreparedStatement对象并执行。减少 SQL 编译次数,提高效率。- 安全性更高,没有SQL输入的隐患
- 提高了程序的可读性
后期都会使用PreparedStatement来完成增删改查的所有操作
8. JDBC的事务操作
事务:一个包含多个步骤的业务操作。如果这个业务操作被事务管理,则这多个步骤要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
使用
Connection对象来管理事务- 开启事务:
setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit):调用该方法设置参数为fasle,即开启事务 - 提交事务:
commit() - 回滚事务:
rollback()
- 开启事务:
8.1 银行转账案例
步骤分析:
- 获取连接
- 开启事务
- 获取到PreparedStatement
- 使用PreparedStatement执行两次更新操作
- 正常情况下提交事务
- 出现异常回滚事务
- 释放资源
public class EFT {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps1 = null;
PreparedStatement ps2 = null;
try {
// 1. 获取连接
conn = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false); // 将自动提交关闭,即开启事务
// 定义sql,小张-500
String sql1 = "update account set balance = balance - ? where name = ?";
// 小李+500
String sql2 = "update account set balance = balance + ? where name = ?";
// 获取执行sql对象
ps1 = conn.prepareStatement(sql1);
ps2 = conn.prepareStatement(sql2);
// 给?赋值,小张-500
ps1.setDouble(1,500);
ps1.setString(2,"小张");
ps1.executeUpdate(); // 执行更新语句
// 给?赋值,小李+500
ps2.setDouble(1,500);
ps2.setString(2,"小李");
ps2.executeUpdate(); // 执行更新语句
// 手动制造一个异常
int i = 3/0;
// 提交事务
conn.commit();
System.out.println("事务执行完毕");
} catch (Exception e) {
// 事务的回滚
try {
if (conn != null)
System.out.println("事务异常!回滚中....");
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
// 释放资源
JDBCUtils.close(ps1,conn);
if (ps2!=null){
try {
ps2.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
- 能够理解JDBC的概念
- 能够使用DriverManager类
- 能够使用Connection接口
- 能够使用Statement接口
- 能够使用ResultSet接口
- 能够说出SQL注入原因和解决方案
- 能够通过PreparedStatement完成增、删、改、查
- 能够完成PreparedStatement改造登录案例
- 能够完成JDBC事务操作

